|
Downloads: 14 | Size:
2015_Mainstreaming Climate Change Into Integrated Water Management Planning for Uganda _Proposed revisions of the Mpanga Catchment Management Plan (D1)In 2008, the Directorate of Water Resources Management (DWRM) and the Ministry of Water and Environment (MWE) adopted a strategy to deconcentrate IWRM at the regional and river basin or catchment level with central oversight and guidance. One of the mains reasons behind this strategy is that it brings IWRM functions closer to stakeholders (farmers, townspeople, local government officials, etc.). Doing this helps to concentrate the focus onto real problems, to improve the analytical underpinnings of programs and projects and it also provides the opportunity for stakeholders to participate in the formulation of plans and the development of new water infrastructure. |
|

|
Downloads: 18 | Size:
Irrigation Development in Uganda_Constraints, Lessons Learned, and Future PerspectivesPolicy makers in sub-Saharan African (SSA) countries have identified irrigation as a key ingredient to boosting food security and income as well as a precursor for agricultural development. However, most SSA countries have hardly exploited their irrigation potential. The overarching aim of this paper is to critically examine factors constraining exploitation of irrigation potential in Uganda. Lessons learned from previous interventions and successes elsewhere from countries comparable to Uganda are drawn and future perspectives to guide effective irrigation planning and development are recommended. From this paper, it is evident that there is no single blanket solution to constraints of irrigation development in SSA. All strategies should be implemented in a holistic manner dictated by specific local conditions. The key to successful adoption of irrigation lies in building the national irrigation capacity, improving access to reliable water for irrigation in proximity of the farms, streamlining extension services for farmers, addressing economic aspects of irrigation, and streamlining land tenure systems and management. It is recommended to operationalize government policy on irrigation by developing national guidelines on irrigated agriculture. |
|

|
Downloads: 23 | Size:
Uganda Catchment Management Planning Guidelines-revised-Sep2017These guidelines were prepared by the Directorate of Water Resource Management of the Ministry |
|

|
Downloads: 12 | Size:
Pro-Poor Strategy Review Uganda – final for Ops Portal May 2015This volume is a product of the staff of the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development/ The World Bank. The findings, interpretatioand conclusions expressed in this paper do not necessarily reflect the views of the Executive Directors of The World Bank or the governments threpresent. The World Bank does not guarantee the accuracy of the data included in this work. The boundaries, colors, denominations, and otinformation shown on any map in this work do not imply any judgment on the part of The World Bank concerning the legal status of any territor the endorsement or acceptance of such boundaries. |
|

|
Downloads: 13 | Size:
Economic Study 2018-Contribution of Water Development and Environment Resources to Ugandas EconomyThe study is a partnership between the Industrial Economics (IEc) expert team and staff, |
|

|
Downloads: 16 | Size:
Economic Study for Water and Environment Sector-Uganda Factsheet A3This analysis models the GDP effects of MWE investment across ten channels of economic impact. First, biophysical and reduced form models are employed to understand the impacts of management decisions. The results of these models are then input to an economy-wide model to estimate the overall economic impacts of MWE investment. |
|

|
Downloads: 15 | Size:
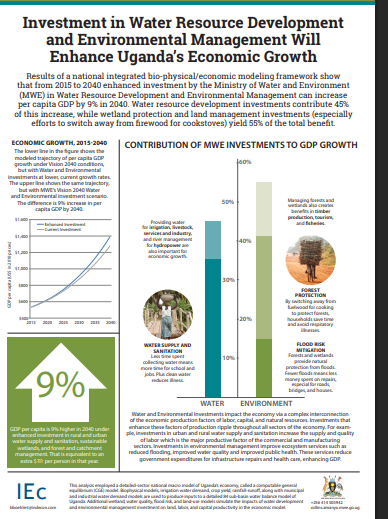
Economic Study for water and environment sector-Uganda Factsheet A4Results of a national integrated bio-physical/economic modeling framework show |
|

|
Downloads: 7 | Size:
Environmental and Social Commitment Plan (ESCP) – November 2020 |
 Official Website of the Ministry of Water and Environment
Official Website of the Ministry of Water and Environment